FPGA Hardware Acceleration over PCIe
What This Is
Multi-threaded Linux application + custom kernel driver + FPGA hardware design that accelerates Sobel edge detection on images. Demonstrates full-stack embedded systems engineering from RTL to application layer.
Project Summary
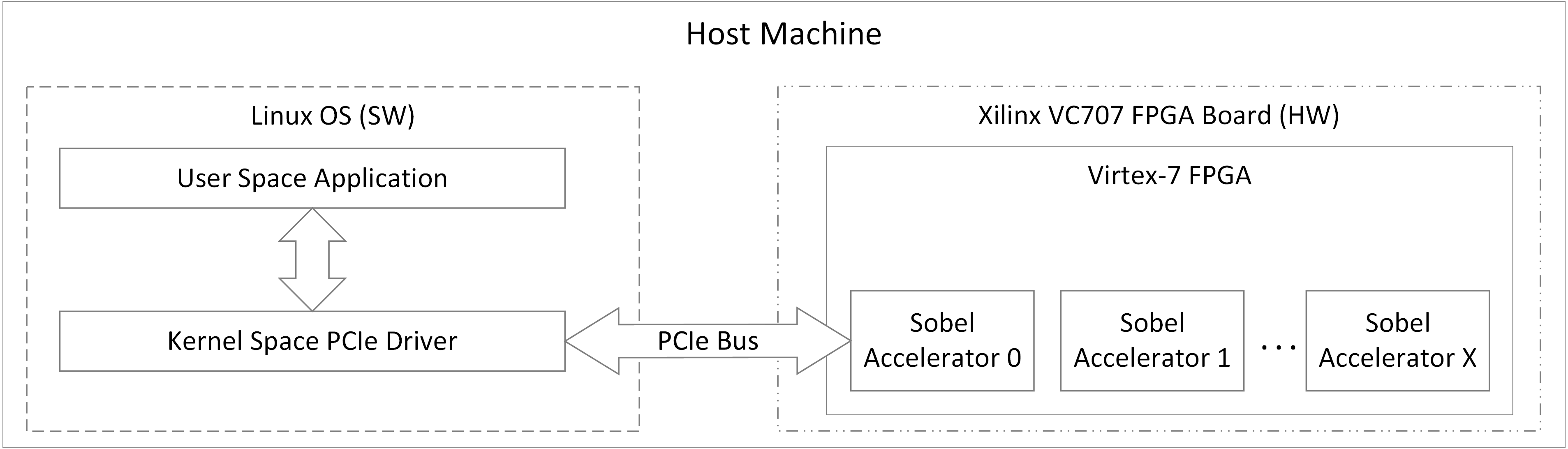
This project implements a full-stack hardware acceleration platform that offloads compute-intensive image processing tasks from a multi-threaded Linux application to custom FPGA accelerators connected via PCIe. The system demonstrates advanced concepts in computer architecture, hardware-software co-design, parallel processing, and driver development.
Key Achievement
Successfully designed and implemented a multi-acceleration-group architecture supporting concurrent hardware acceleration for up to 16 simultaneous threads, with intelligent resource scheduling and DMA-based data transfers.
Technical Overview
Hardware (Xilinx Virtex-7 FPGA)
- 7 parallel acceleration units supporting up to 16 concurrent threads
- Custom IP cores designed in C/C++ (Vivado HLS), synthesized to RTL
- PCIe Gen2 x4 interface with DMA engines for high-throughput data transfer
- Sobel filter accelerator processing up to 1080p images
Software (Linux)
- Kernel driver: PCIe device management, MSI interrupts, multi-thread resource scheduling
- User application: pthreads, memory-mapped I/O, DMA buffer management
- MicroBlaze firmware: FPGA system initialization
Architecture Highlights
┌─────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ Multi-threaded Application (pthreads) │
└──────────────┬──────────────────────────┘
│ ioctl(), mmap()
┌──────────────▼──────────────────────────┐
│ Kernel Driver (Resource Scheduler) │ ← Thread arbitration, DMA setup
└──────────────┬──────────────────────────┘
│ PCIe, MSI Interrupts
┌──────────────▼──────────────────────────┐
│ FPGA Hardware (7 Accel Groups) │ ← Parallel processing
│ • Fetch/Send Schedulers (DMA) │
│ • Sobel Filter Accelerators │
│ • Interrupt Manager │
└─────────────────────────────────────────┘
Why 7 acceleration groups?
- 2 Direct-mode (PCIe → BRAM, low latency)
- 4 Indirect-mode (PCIe → DDR3, higher throughput)
- 1 Scatter-Gather (supports fragmented user memory)
Each can process different images simultaneously with driver-managed scheduling.
Engineering Challenges Solved
1. Multi-thread resource arbitration
16 threads competing for 7 hardware units → Implemented two scheduling policies (greedy, best-available) in kernel driver with per-thread state tracking
2. PCIe interrupt routing
Designed custom Interrupt Manager IP to map 7 accelerators to MSI vectors, coordinated with GPIO-triggered interrupts
3. Zero-copy DMA from userspace
Used get_user_pages() + scatter-gather tables for direct DMA to/from application buffers without memcpy overhead
4. Hardware-software timing correlation
FPGA global timer accessible via memory-mapped registers for nanosecond-precision performance analysis
Results
- Throughput: Supports 16 concurrent requests with linear scaling up to 7 threads
- Latency: ~50-100 μs for VGA images (640x480)
Quick Start
# Generate custom IPs (one-time)
cd Hardware/Vivado_HLS_IPs/Sobel_Filter && vivado_hls run_hls.tcl
# ... repeat for 8 other IPs
# Build bitstream
cd Hardware && vivado -source create_project.tcl
# Flow → Generate Bitstream
# Load driver & run
cd Software/Linux_App_Driver
make
./make_device
insmod xilinx_pci_driver.ko
./ui image. bmp 100 16 1 10 # 100 iterations, 16 threads
Repository Structure
Hardware/Vivado_HLS_IPs/ 9 custom IP cores (C++ → RTL)
Hardware/Vivado_Block_Design/ System integration (AXI, PCIe, DDR3)
Software/Linux_App_Driver/ Kernel driver + test application
Software/Microblaze_XSDK/ FPGA firmware